➲ Home ➲ C-19 Archives
☰ 8 studies & articles on... SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) vaccines, ‘Omicron’, and waning protection
‘Vaccine effectiveness against SARS-CoV-2 [COVID-19] infection declines markedly with time and Omicron variants.’
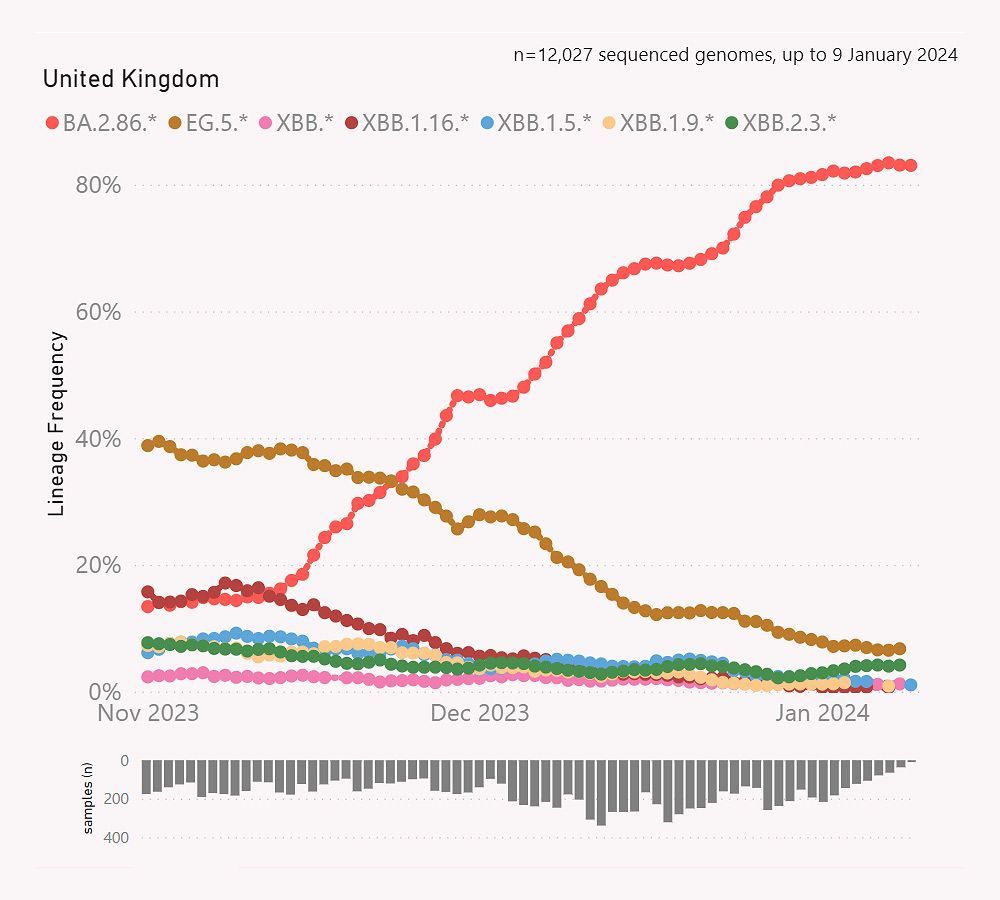
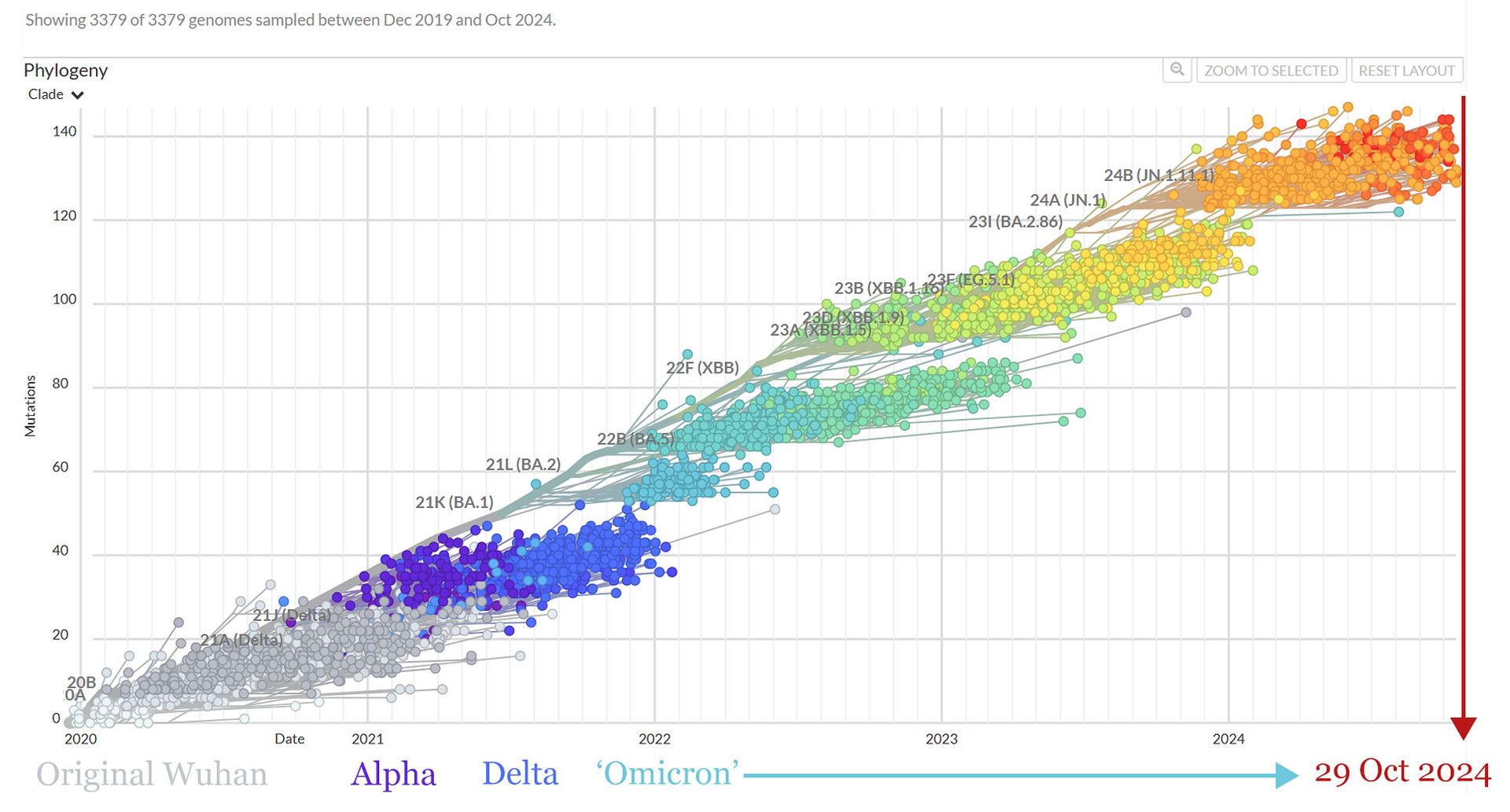
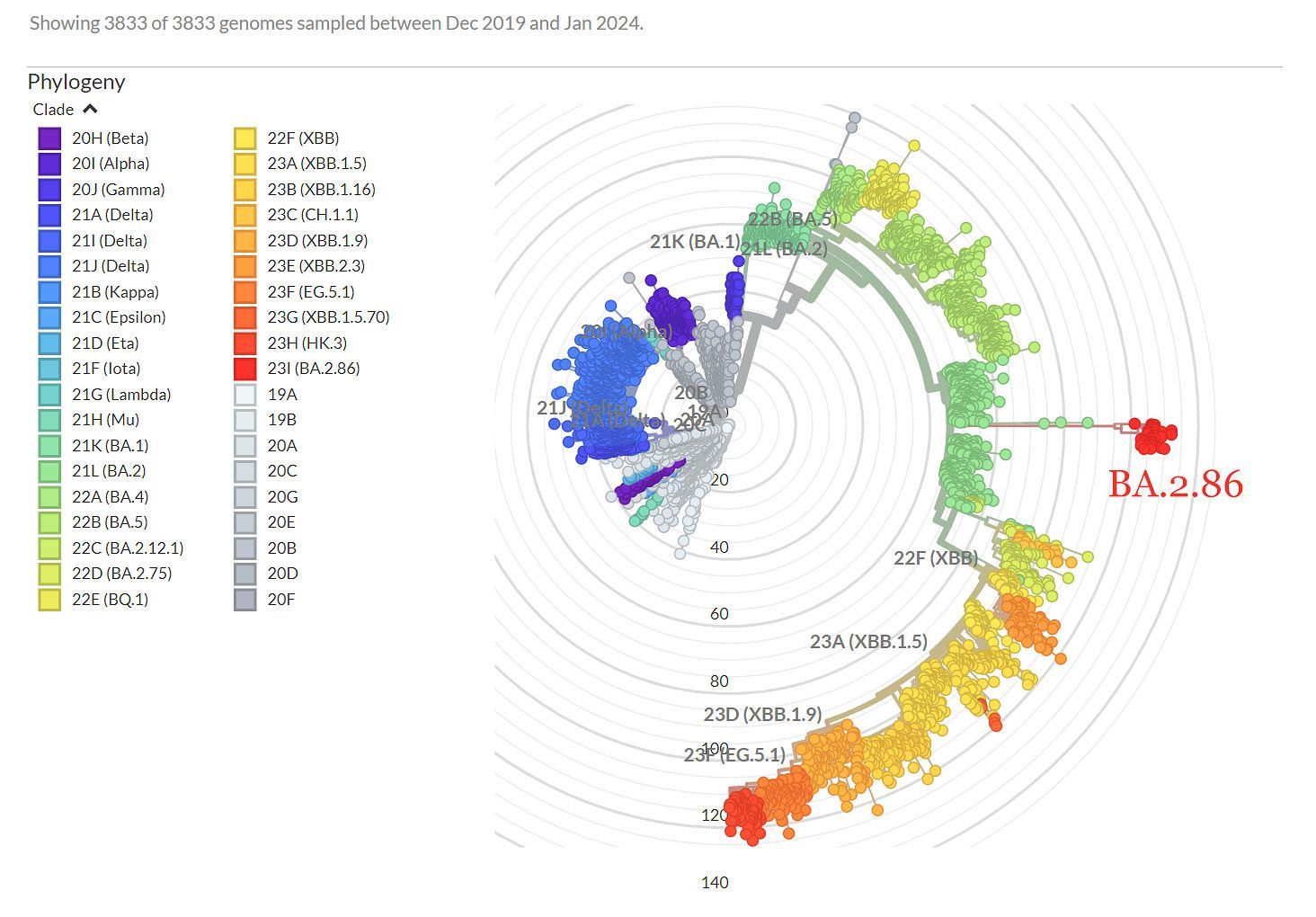
❦ SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) variants of concern (VOC) by date.
➲ Date accessed: 29 October 2024.
➲ Genomic epidemiology of SARS-CoV-2 since pandemic start.
© 2024 NextStrain.org.
❂
❦ On waning vaccines, and the ‘Omicron’ variant (late 2021–)
📖 (9 Apr 2025 ~ Pharma Times) NHS launches spring COVID-19 booster campaign ➤
‘Eligible [UK] groups are being offered an additional [‘COVID-19 vaccine booster’] to increase protection against the virus. These include everyone aged 75 years and over, residents of older adult care homes, and people aged six months and over with weakened immune systems.
Alex Allen, consultant epidemiologist at the UK Health Security Agency [UKHSA], said last year’s spring programme proved effective. “It reduced the risk of getting severely ill and being hospitalised by over 40% in those at greatest risk – for up to nine weeks after vaccination.”’
© 2025 Ella Day / Pharma Times Online.
📖 (27 Feb 2025 ~ CDC) Interim Estimates of 2024–2025 COVID-19 Vaccine Effectiveness Among Adults Aged ≥18 Years — VISION and IVY Networks, September 2024–January 2025 ➤
‘Vaccine effectiveness (VE) of 2024–2025 COVID-19 vaccine was 33% against COVID-19–associated emergency department or urgent care visits among adults aged ≥18 years, and 45%–46% against hospitalizations among immunocompetent adults aged ≥65 years, compared with not receiving a 2024–2025 vaccine dose.
VE against hospitalizations in immunocompromised adults aged ≥65 years was 40%.’
© 2025 Link-Gelles et al / The USA’s Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
📖 (19 Feb 2025 ~ European Respiratory Review) Effectiveness of COVID-19 vaccines against SARS-CoV-2 infection and severe outcomes in adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis of European studies published up to 22 January 2024 ➤
‘Vaccine effectiveness against SARS-CoV-2 [COVID-19] infection declines markedly with time and Omicron variants.’
© 2025 Zhou et al / European Respiratory Review.
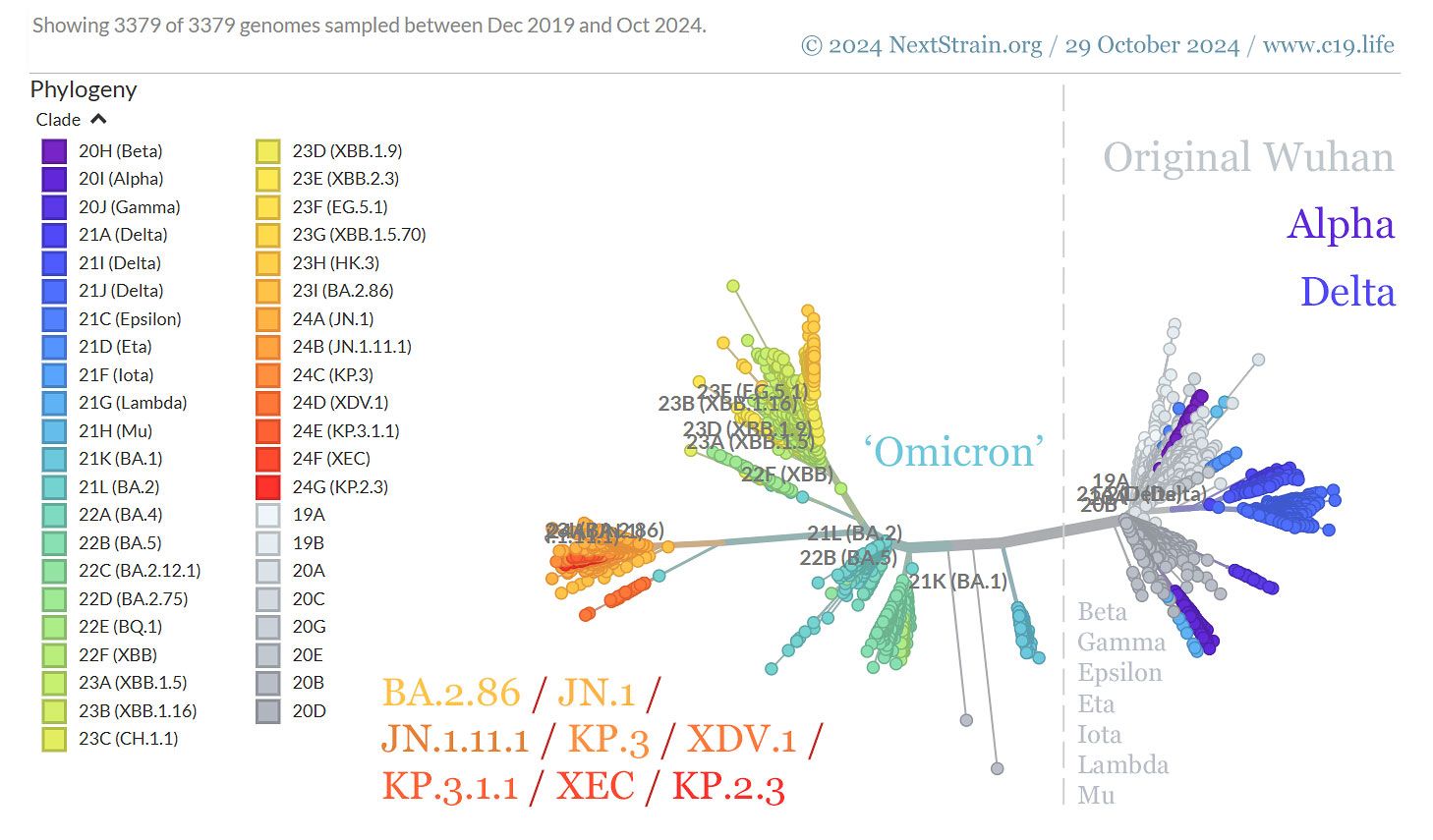
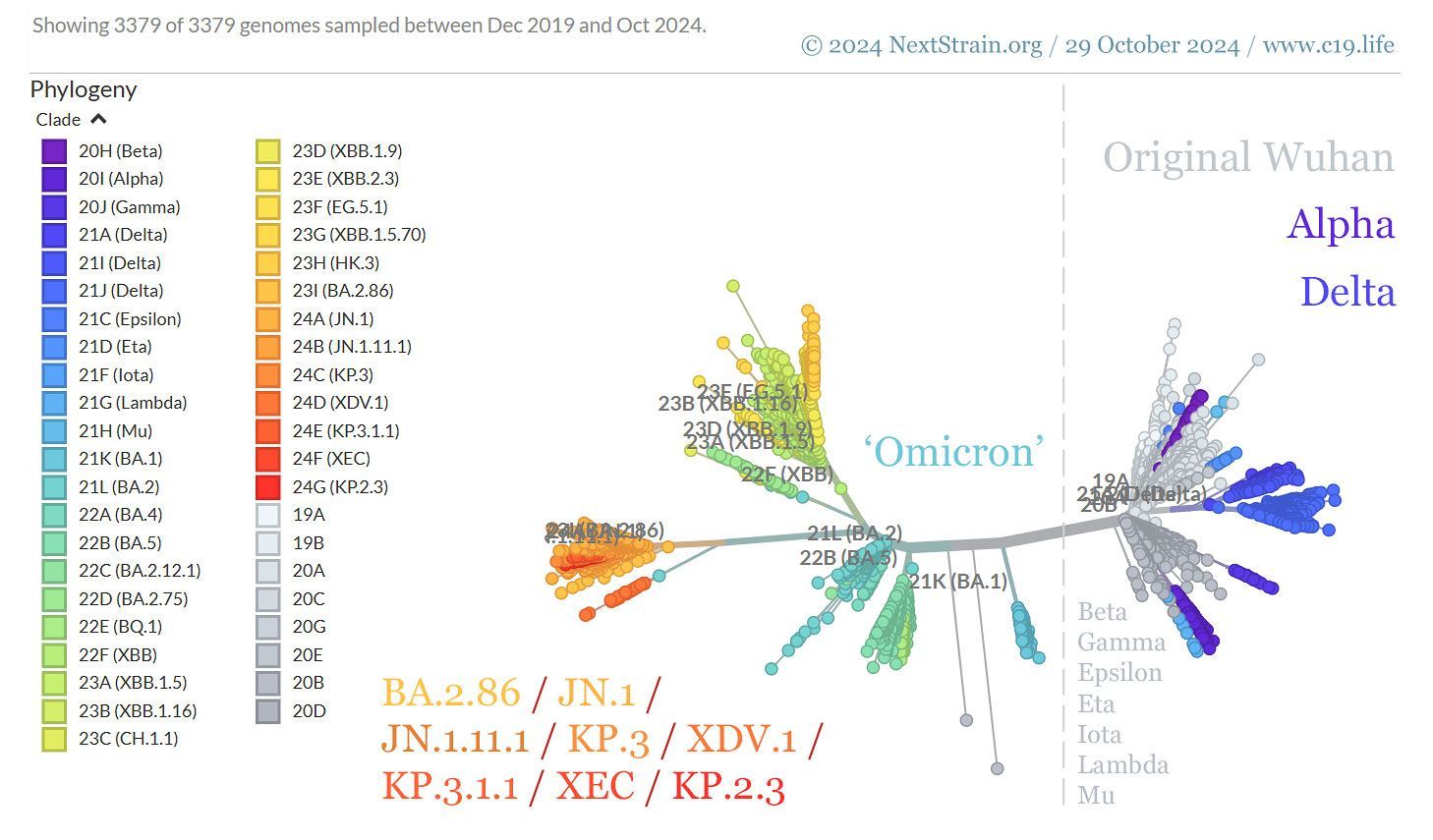
❦ SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) variants of concern (VOC).
➲ Date accessed: 29 October 2024.
➲ Genomic epidemiology of SARS-CoV-2 since pandemic start.
© 2024 NextStrain.org.
📖 (5 Feb 2025 ~ Nature) Differential protection against SARS-CoV-2 reinfection pre- and post-Omicron ➤
‘The arrival of the Omicron variant [in late 2021] marked a major shift, introducing numerous extra mutations in the spike gene compared with earlier variants.
These evolutionary changes have raised concerns regarding their potential impact on immune evasion, disease severity and the effectiveness of vaccines and treatments.’
© 2025 Chemaitelly et al / Nature.
📖 (6 Aug 2024 ~ Clinical Infectious Diseases) Effectiveness of Updated 2023–2024 (Monovalent XBB.1.5) COVID-19 Vaccination Against SARS-CoV-2 Omicron XBB and BA.2.86/JN.1 Lineage Hospitalization and a Comparison of Clinical Severity—IVY Network, 26 Hospitals, 18 October 2023–9 March 2024 ➤
‘Omicron BA.2.86 and its descendants, including JN.1 (referred to as ‘JN lineages’), emerged in late 2023 and exhibited substantial divergence from co-circulating [Omicron] XBB lineages.
Vaccine effectiveness in the first 7–89 days after receipt of an updated [2023–2024 monovalent XBB.1.5 vaccine] dose was 54.2% against XBB lineage hospitalization, and 32.7% against JN lineage hospitalization.’
© 2024 Ma et al / Clinical Infectious Diseases.
📖 (1 Aug 2024 ~ JAMA Internal Medicine) Estimated Effectiveness of the BNT162b2 XBB Vaccine Against COVID-19 ➤
‘Effectiveness... of the [Pfizer] BNT162b2 XBB vaccine was 62% against COVID-19 hospitalization, and 58% for Emergency Department or Urgent Care visits.
Older versions of COVID-19 vaccines offered little, if any, long-term protection, including against hospital admission, regardless of the number or type of prior doses received.’
© 2024 Tartof et al / JAMA Internal Medicine.
Nb. Conflict of Interest Disclosures:
Dr Tartof reported institutional grants from Pfizer and GSK outside the submitted work. Dr Slezak reported institutional grants from Pfizer and Dynavax outside the submitted work. Mr Frankland reported a research contract with Pfizer and previous stock in Pfizer. Dr Puzniak reported personal fees from Pfizer during the conduct of the study. Ms Hong reported institutional grants from Pfizer during the conduct of the study. Dr Ackerson reported institutional grants from Pfizer, Moderna, GSK, and Dynavax outside the submitted work. Dr Stern reported grants from GSK, Sanofi, and Moderna outside the submitted work. Dr Jodar reported salary from and stock in Pfizer outside the submitted work. Dr McLaughlin reported salary from and stock in Pfizer during the conduct of the study. No other disclosures were reported.
“No other disclosures were reported.”
Well, thank goodness for that.
Maybe that’s why they had to end the piece with ‘...the BNT162b2 XBB vaccine provided statistically significant additional protection against a range of COVID-19 outcomes.’
Like what – having an itchy earlobe?
If 60:40 is significant protection against an A&E visit or hospital admission, I’d hate to see the odds for insignificant protection.
📖 (29 May 2024 ~ The New England Journal of Medicine) Durability of XBB.1.5 Vaccines against Omicron Subvariants ➤
‘The [Omicron XBB.1.5] vaccine effectiveness against infection reached a level of 52.2% after 4 weeks. It decreased to 32.6% after 10 weeks and to 20.4% after 20 weeks.
The effectiveness against hospitalization reached a level of 66.8% after 4 weeks, and decreased to 57.1% after 10 weeks.
The [Omicron] XBB.1.5 vaccines were less protective against [Omicron] JN.1 than against XBB sublineages.’
© 2024 Lin et al / The New England Journal of Medicine.
📖 (25 May 2022 ~ Nature: Medicine) Long COVID after breakthrough SARS-CoV-2 infection ➤
‘Vaccination before infection confers only partial protection in the post-acute phase of the disease.’
© 2022 Al-Aly, Bowe & Xie / Nature: Medicine.
❂
More... On variants, immunity and vaccines
More... On reinfections
❂
C-19: Archives
Useful search tags:
air filtration / babies & children / body / brain / C19.Life / cancer / comment / dementia / economy / elders / excess deaths / exercise / flu / heart / history / hospitals / immunity / influenza / law / Lisa Iannattone / long covid / lungs / mitochondria / muscles / musculoskeletal / NHS / Noor Bari / nosocomial / PEM / parkinson’s / propaganda / reinfections / reproduction and pregnancy / resources / respirators / respiratory / risk / SARS(-CoV-1) / schools / solutions / transmission / universities / UVC / vaccines / variants / WHO / young adults / zoonosis